Climate Change Impacts Public Safety
Climate Change: SAFRR is proactive in its work to make communities more resilient as hotter weather - compounded by high winds – is resulting in devastation from wildfire, ember cast and structure to structure ignitions.
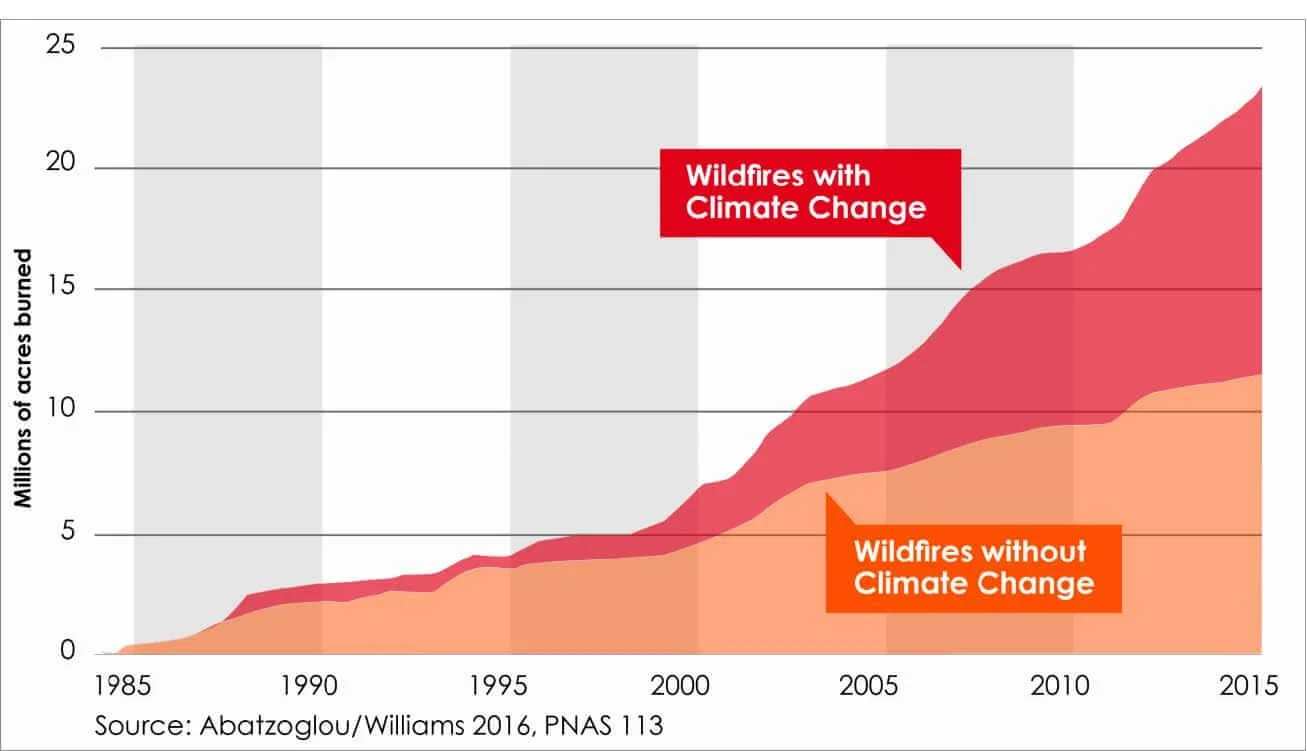
Figure - 013: Wildfires and Climate Change: California’s Energy Future: A Report from Governor Newsom’s Strike Force April 12, 2019
SAFRR recommends that local emergency plans utilize fire behavior modeling.
A paper by Carol Rice titled Clarify Evacuation Options through Fire Behavior and Traffic Modeling outlines the mutual benefits of these studies.
PERIL Modeling Framework - A fire behavior study models the wind and other factors that impact the advance of wildfire through various terrains. Then, it defines scenarios from typical wind to enhanced-wind conditions, contrasting scenarios of expected wildfire speed to determine the time it may take for the community and/or evacuation routes to burn over, as compared to the speed of evacuation traffic and expected time to reach a safe zone.
LEARN MORE: